One of the most common legacy ethernet standards is the 100BASE-TX specification. This ethernet standard is limited to a max speed of 100 Mbps. This used to be incredibly fast. Today it is slower than many of the newer Wi-Fi standards and many people’s home broadband internet connections.
The current most commonly used 1000BASE-T ethernet standard supports up to 1 Gbps per second, and newer ethernet standards support speeds of 2.5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, or even 40 Gbps.
This is faster than modern Wi-Fi standards. If your Wi-Fi speed is currently faster than your ethernet speed, it is likely due to your ethernet running at 100 Mbps or, worse, 10 Mbps. The following are the most common reasons for ethernet to run at slower speeds.

Reasons Your WiFi is Faster than Ethernet

Your Computer’s Ethernet Port Supports a Maximum of 100 Mbps
Many older desktop and laptop computers were commonly equipped with ethernet ports that maxed out at 100 Mbps. At the time, this was considered fast enough, and only more expensive models included gigabit ethernet ports.
Today, 100 Mbps is slower than many people’s home broadband internet connections. Modern Wi-Fi standards, including Wi-Fi 6 (802.11-ax) and Wi-Fi 5 (802.11-ac), commonly support real-world speeds well in excess of 100 Mbps. Unfortunately, as recently as 2018, there were computers that were still selling with 100 Mbps ethernet ports.
The easiest way to confirm the specs of your ethernet card is to look in Device Manager on Windows. To open Device Manager, type Device Manager into the Windows taskbar search bar. After opening Device Manager, look for your ethernet adapter. Click to expand its details.
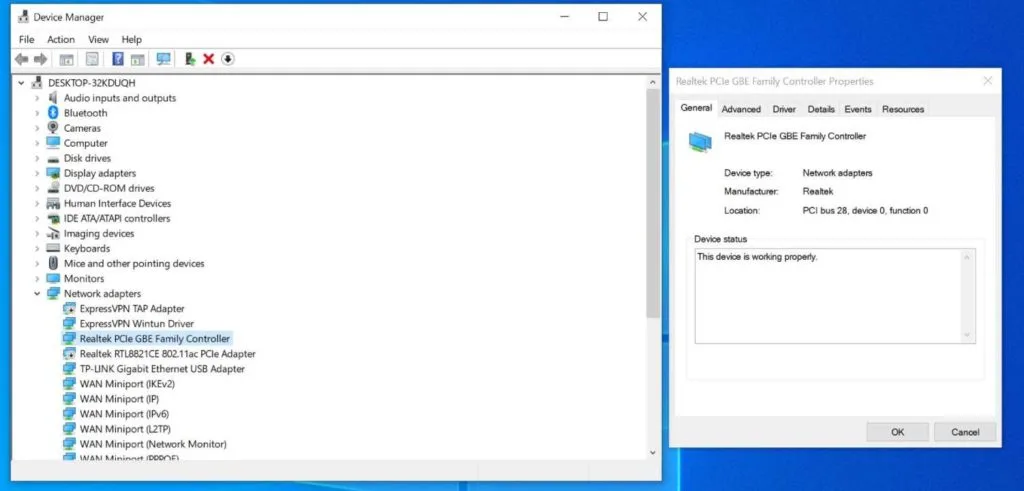
You will then likely see a reference to either fast ethernet or gigabit ethernet. Fast ethernet means 100 Mbps, gigabit ethernet means 1000 Mbps. If you do not see either listed, you can simply search the model of your ethernet adapter on the web and find out its maximum speed.
If your ethernet card supports gigabit speeds, you are in good shape, and this is not the cause of your slowness.
If your ethernet card is limited to fast ethernet (100 Mbps) speeds, you will not be able to get faster speeds through that connection. Your options at that point would be either to accept the lower speeds, switch to using Wi-Fi, purchase a PCIe gigabit ethernet card, or purchase a USB 3 gigabit ethernet adapter.
Fortunately, these upgrades are surprisingly affordable. Here are my recommendations for PCIe and USB Adapters from Amazon.
TP-Link Gigabit Ethernet PCIe Network Card

Anker USB 3.0 to Gigabit Ethernet Adapter

In addition to computers, there are other devices that are limited to 100 Mbps by the ethernet port used on them. These can include older game consoles, streaming boxes, etc. If your device is using a 100 Mbps ethernet port on it, you will not see faster speeds on that device.
Your Network Router Or Switch Supports a Maximum of 100 Mbps
Another common reason for slower ethernet speeds is because of an older router or network switch that maxes out at 100 Mbps. The best way to determine if this is the problem is to search your router or switch’s model on the internet and find its ethernet port specs. If your router or switch supports gigabit ethernet, it is not likely the issue. Just to be certain, you should try plugging the cable into a different port on your router or switch.
If your router or switch maxes out at 100 Mbps, it is going to limit you to that speed. Chances are if your router or switch maxes out at 100 Mbps, it is likely older and due to be upgraded anyways. A quality router is an essential part of any network and not a place to try and cheap out.
Prices have declined in recent years, your options are numerous. There are many great options out there.
If you have decided that it is time to upgrade your router, please check out the Amazon links below to see my current recommendations.
Top Budget Pick: TP-Link WiFi 6 Router AX1800

Top Overall Pick: Linksys AX6000 Smart Mesh Wi-Fi 6 Router

Your Ethernet Cable Is Damaged
A properly functioning Category 5e (Cat 5e) or higher ethernet cable will reliably support speeds of up to 1 Gbps at distances of up to 100 meters (328 feet). There is absolutely no need to use expensive Cat 7 or Cat 8 cables to get optimal performance.
Ethernet cables can wear out or get damaged. When ethernet cable damage happens, it can easily become the source of a number of connectivity issues.
One common issue is speeds dropping from 1 Gbps down to 100 Mbps or even 10 Mbps. This is because the lower data transmission rates are more forgiving of errors in the signal. If your cable is faulty, very often, your computer will automatically try connecting at a reduced speed in an effort to maintain a usable connection at all.
If the ends of your ethernet cable get damaged, you may lose connectivity on one or more of the pins. The gigabit standard requires all 4 pairs of wires for connectivity. The older 100 Mbps ethernet standard only uses pins 1,2,3,6. If pins 4,5,7, or 8 get damaged, your connection will automatically negotiate at 100 Mbps, and that will limit your speeds from going higher.
Fortunately, if this is the case, there are many quality, affordable ethernet cables from trusted manufacturers. If you would like to try replacing your ethernet cables, please check out my Amazon links below to see my current recommendation.
Best Ethernet Cable: Cable Matters Snagless Cat6 (Choose Your Length)


Your Ethernet Driver Software Is Not Working Properly
Your ethernet driver software can sometimes have an issue that affects your connection speed. This is not as common as the previous causes listed above but does happen from time to time. If you noticed the issue began after a major Windows update or after installing some new software, this is especially likely.
If your ethernet driver software needs to be updated, the two best places to download an updated driver from are either the manufacturer of your computer or the manufacturer of your ethernet card. Many times this will be either Realtek, Broadcom, or Intel. If you are unsure, check in Device Manager to find the make and model of your ethernet card.
Alternatively, you can often go to the manufacturer of your computer and run their automatic hardware detection tool. The hardware detection tools Dell and HP provide work exceptionally well in most cases. I highly recommend starting here if you have an HP or Dell computer.
Generally, I would recommend avoiding using Windows update to download and install driver updates, and most importantly, I would never ever recommend downloading any 3rd party driver update utility. These are almost always laced with malware and should be avoided at all costs.
After installing your updated driver, restart your computer before retesting your connection speed.
Interference Is Impacting Your Ethernet Signal
Another possible cause of your ethernet running at 100 Mbps or 10 Mbps is signal interference. Although interference is much more common with wireless networks, in some cases, it can also impact wired networks.
The most common issue is when ethernet cables are run for long distances directly beside AC electrical wiring. This is an especially common issue when they are run through the same conduit, often through ceilings or underground.
If this is the case, you may have no other options other than to either separate the ethernet cables from the AC wiring or to run new ethernet cabling. If this is not possible, you may have to simply live with the reduced throughput or look at other communication protocols.
One option if you must run your data in very close proximity to your AC wiring is to use fiber optic cables. Fiber optic communication uses light inside of glass fibers and is, therefore, 100% immune to electrical interference.
Other common interference sources include fluorescent lighting, large electric motors, and power inverters. If ethernet cables are run in close proximity to these devices, it is much more likely to have issues with signal interference.
Your Router or Ethernet Adaptor is Set to 10/ 100 Mbps
In most cases, it is possible to change the ethernet link speed manually. It is possible that you may have in the past changed that from automatic to 10 /100 Mbps only. This will force your ethernet connection to operate at a slower speed.
You can fix this by enabling auto-negotiation on your router and on your ethernet adaptor. Alternatively, you could manually specify 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps) manually. You may have accidentally changed this setting without realizing it.
Conclusion: Why is My WiFi Faster than Wired
These are the most common reasons that your Wi-Fi may be faster than your ethernet. In many cases, there is an easy fix. Give the things listed in this article a try. These are the most likely things to cause your ethernet to be slower than your WiFi connection. In other cases, there is nothing you can practically do about it. Not every device with an ethernet port supports higher speeds.
If you run into this situation and are still wondering why is my wifi faster than ethernet, you will have to decide if you want to use Wi-Fi or ethernet. In some cases, it might make sense to continue using ethernet even if your Wi-Fi is faster. Oftentimes time, the stability of ethernet is what matters most.
This is especially true for gaming. Despite what most people think, online gaming only requires about 5 – 10 Mbps of bandwidth for optimal operation. Ping and stability are what counts, and for that, ethernet is almost always the better choice.
If fast downloads are your top priority and you can’t fix your issue, you may want to use WiFi if it is faster in your situation. Just note that the thing about WiFi is that it can be inconsistent in performance. For example, when your microwave oven is used, you may see interference.
