Starlink does not offer static IP addresses on any of its plans. The type of IP address that you will get depends on what Starlink plan you subscribe to. Unfortunately, at this time, none of them offer a true static IP address like you would get from a business-class cable or fiber internet connection.
Static IP addresses are important to some business users who host web servers or email servers on-premise. Externally facing servers need IP addresses that don’t change.
| Type of IP Address Offered | |
| Starlink Residential | CGNAT Only |
| Starlink Roam (Formerly Starlink for RVs) | CGNAT Only |
| Starlink Business | CGNAT or Dynamic Publicly Routable |
| Starlink Maritime | CGNAT or Dynamic Publicly Routable |
Starlink IP addresses come in two distinct varieties depending on which Starlink plan you use.
Starlink Residential and Starlink Roam (formerly Starlink for RVs) get assigned Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CGNAT) IP addresses via DHCP from Starlink’s 10.64.0.0/10 network. Routing internal to Starlink’s core network translates between your CGNAT private IP address and a real public IP address. With this setup, hundreds or even thousands of Starlink subscribers can be sharing the same public IP address and not even know it.
Starlink Business and Starlink Maritime customers have the option of enabling a public routable IP address on their accounts. According to Starlink’s official support page, Starlink gives us the following information.
“A public IP is reachable from any device on the internet and is assigned to Starlink network clients using DHCP. Moving the Starlink to another location may cause the public IP to change.“
There is no mention of a Static IP (also known as a fixed IP) address being offered even to business users.
Table of Contents
Starlink Public IP
What does Starlink really mean when they say that Starlink Business customers have the option of a publicly routable IP address? A public IP address simply means any IP address that is accessible via the internet from outside of the Starlink network.
A public IP address is not a unique thing to Starlink. Most internet service providers (ISP) include a public IP address with all internet plans, including most residential plans. The benefit of a public IP address is that it can accept traffic from the outside.
For example, if you need to use port forwarding or host a VPN server on your network, you would need a public routable IP address. Without a public IP, you have no means of directing traffic in from the outside world.
Public IP addresses fall outside of these IP ranges. These are defined by RFC 1918 and RFC 6598.
- Class A: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- Class B: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- Class C: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
- CGNAT: 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255
What is a CGNAT IP Address
Carrier-grade network address translation (CGNAT) is a technique that allows ISPs to have hundreds or even thousands of users, all sharing a single public IP address.
The way CGNAT works is very similar to how NAT works on your router, it just runs on a large scale. CGNAT is also sometimes referred to as large-scale NAT.
CGNAT works by assigning you a private IP address rather than a public IP address. For many residential internet users, CGNAT will cause zero issues. Web browsing, email, video streaming, social media, online shopping, online banking, etc., all work problem free with CGNAT.
CGNAT causes issues for applications that need to allow connections from the outside. Common examples include P2P applications, online gaming, and anything that requires port forwarding to be configured on your router.
With CGNAT, port forwarding is not possible, as there is no way for external traffic to reach your router. If you need port forwarding, you need a public IP address.
CGNAT is most commonly used by cell phone carriers and satellite internet providers. If you have internet service with one of the following ISPs, you are likely using CGNAT.
- T-Mobile Home Internet
- Verizon 5G Home Internet
- HughesNet
- Viasat
- Starlink
Of course, there are many others. Most tend to be either cellular or satellite internet service. However, in developing countries, CGNAT is more commonly used by all ISPs. There is a shortage of IPv4 addresses, and CGNAT is a workaround until IPv6 fully becomes the norm.

How to Tell if You Have a Public IP
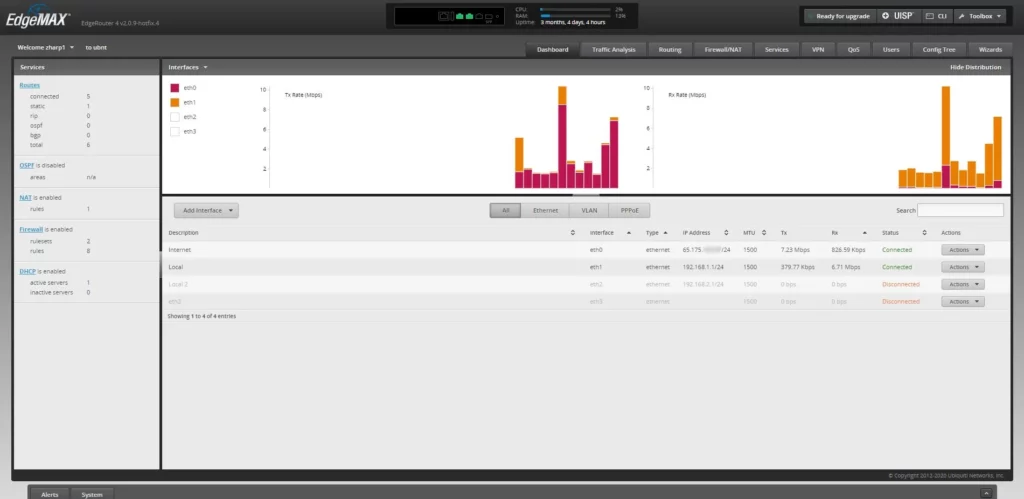
The easiest way to tell if you have a public IP address assigned to you is to look at router settings. Find the WAN/Internet interface of your router and look at the IP address assigned to it. Is it in one of the IP ranges listed above?
Then visit a site such as whatismyip.com and compare the result to what your router lists as the IP address being used by your WAN connection.
If they match, you have a public IP assigned to you, and your ISP is not using CGNAT. If they do not match, there is a good chance that your ISP is using CGNAT. This is especially true if your router has one of the RFC 1918 or RFC 6598 IP addresses assigned to it.
What is a Static IP Address
A static IP address, also known as a fixed IP address, is simply an IP address that doesn’t change. Static IP addresses are commonly included or available as an add-on with most business-class internet connections.
For example, a static IP is either included or sold as an add-on to business internet plans with the following internet providers.
- Comcast Business
- Spectrum Business
- AT&T Business
- Verizon Business
- Virgin Media
- Consolidated Communications Business
- FirstLight Fiber Business
The list goes on and on. Most business internet plans are available with static IP addresses. Starlink Business is the exception and not the norm.
It is important to note that a public IP address and a static IP address are not the same things. Interestingly a static IP does not have to be a public IP. Although most of the time, when an ISP offers a static IP address, that means a static public IP.
On a similar note, a public IP does not have to be Static. Dynamic public IPs are extremely common. In fact, there is a good chance you are using one right now without even knowing it.
What is a Dynamic IP Address
A dynamic IP address is simply an IP address that can change for any reason at any time. Dynamic IPs are provided to you via your ISP using a network protocol known as DHCP. It is a completely automated process that assigns you an IP address.
A Dynamic IP address can be public, or it can be private (CGNAT). Dynamic simply refers to how it is assigned and the fact that it can change without notice.
Dynamic IP addresses are extremely common. Most residential ISPs give subscribers dynamic IP addresses rather than static IP addresses.
A dynamic IP can be publicly routable but doesn’t have to be. Most traditional non-mobile ISPs give residential internet customers dynamic public IPs. If you sign up for residential service with one of the following ISPs, you will get a dynamically assigned publicly routable IP address.
- Verizon Fios
- Xfinity (Comcast)
- Spectrum
- Cox
- AT&T Fiber
- CenturyLink
- Breezeline
- Consolidated Communications
- Virgin Media
- Fidium Fiber
This is just a short list; most residential internet providers assign dynamic IP addresses to their users.
When is a Static IP Necessary
Static IP addresses are generally required when you need to expose devices to the internet directly. This is the most common for business applications. Things that oftentimes require a fixed IP address include:
- Running web servers on premise
- Hosting email servers on-premise
- Certain VoIP phone systems with on-premise servers
- Site to Site VPN
- Limiting network access based on IP address
- Allowing direct access without DNS based solutions
There are other reasons that a static IP address may be required as well. However, with many companies moving most of their IT infrastructure into the cloud, there are also more and more companies that do not necessarily need a static IP address. Site to Site VPN is still a common need for a static IP.
There are some common workarounds for connections without static IP addresses. The most common is dynamic DNS. Dynamic DNS maps your IP address to a domain name and then automatically updates when your IP address changes.
Dynamic DNS is useful but can’t replace a fixed IP in all situations.
Starlink IPv6 Assignments
According to the official Starlink Support page, Each Starlink customer is delegated a /56 IPv6 prefix for network clients. They also note that all clients get assigned an IPv6 address assuming the router is able to support IPv6. They also note that their first-generation router that came with the round Starlink dishes does not have support for IPv6.
All Starlink network clients are assigned an IPv6 address if their router is IPv6 capable. IPv6 is not supported on the early-generation router in the Circular Starlink Kit.
Given that Starlink gives you publicly routable IPv6 addresses, that opens the door to more options. For connections that require a public IP, it is now possible to connect via IPv6.
Full adoption of IPv6 is likely still years away, but Starlink does at least give you the ability to use IPv6 in 2023. This is a step in the right direction, especially if Starlink is not planning to offer Static IPv4 addresses, even to business users.
Conclusion: Static IP With Starlink
Starlink does not offer static IP addresses on any of its plans, including its more expensive business and maritime plans. This is a disappointment given that most business-class internet services all come with either a static IP included or the ability to add on a static IP for a small upcharge.
Starlink uses CGNAT IP addresses for residential customers, which is similar to other satellite internet providers such as HughesNet and Viasat. Most cable, DSL, and fiber internet service providers include a publicly routable IP address with all plans, including residential.
With Starlink, you have to pay over twice the monthly cost just to get a public IP address. This is less than ideal. On the bright side. Starlink now gives everyone a /56 IPv6 prefix that can be used to enable connections from the outside.
Of course, this is far from an ideal solution given that IPv6 support is far from universal across the internet, and IPv6 – IPv4 tunneling solutions are far too complicated for an average Starlink user to set up on their own network.
Starlink should offer a fixed IP address option to business customers if they want to be on par with other internet service providers. As of now, a Starlink static IP is not an option.
