Many ISPs provide each subscriber with one or more publicly routable IP addresses. Some internet service providers, including Starlink and most cellular internet service providers, employ CGNAT to allow numerous users to share one public IP address.

CGNAT Must Know Info
Is Port Forwarding Possible With CGNAT
Port forwarding does not work as intended if your ISP uses CGNAT. Port forwarding works by specifying which specific ports get forwarded to a specific destination. This requires that your router has a publicly routable IP address assigned to it.
With CGNAT, it is not possible to forward ports to any devices. Whether you need to forward ports to an Xbox Series X | S, PS5, Nintendo Switch, a security camera system, etc., it is not possible with CGNAT
A VPN service is the easier way to add a publicly routable IP address to your network if you ISP only offers CGNAT IP addresses.
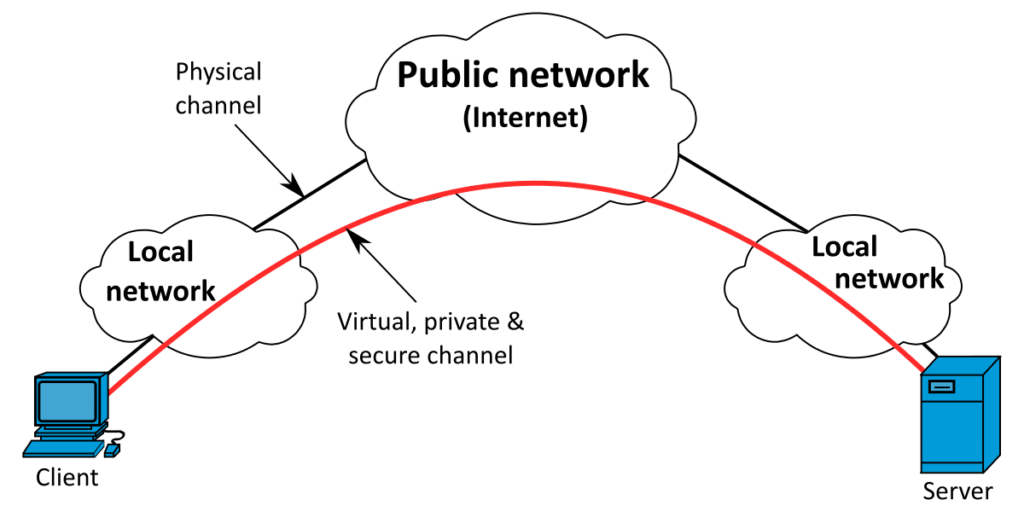
CGNAT Work Around Using a VPN Service
The best way to eliminate CGNAT limitations is to choose an ISP that offers you a publicly routable IP address. This is not always possible. Starlink, HughesNet, Viasat, T-Mobile, etc., do not even offer customers the option of a proper public IP address. If you wish to use one of the services, you will need a workaround if you wish to open up ports to the internet.
The best option is to use a VPN service that provides you with a static public IP address. With a public IP address, you will be able to forward any ports that are required. You can run the VPN client software on your computer. tablet, smartphone, or another device (best for beginners).
The other option is to run the VPN client on your router. You will need a router that has this functionality built into it. The best part about using VPN on your router is now all of your devices can use the VPN connection automatically.
You can then use port forwarding the same way you would with an internet service provider that offers a public IP address, such as Xfinity, Spectrum, or Verizon Fios.
In my experience, NordVPN is the easiest VPN to configure with a static public IP address that can be used to expose ports directly to the internet. Try NordVPN risk free and see if it meets your needs.


Set Up Your Own VPN Server (Advanced Option)
More technically inclined users may want to consider setting up their own VPN server with a public IP address using a service such as Digital Ocean, AWS, or Google Cloud. This is definitely more complicated to set up but offers a few interesting benefits.
By setting up your own VPN server, you are in complete control over your setup. In many cases, it can also be cheaper than using a commercial VPN service such as NordVPN.
Just keep in mind that it is completely up to you to set it up and keep it secure. If something breaks, you are the one who has to fix it. Most people would be better off with a commercial VPN service such as NordVPN.
What is Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT)
The abbreviation CGNAT stands for Carrier Grade Network Address Translation. It’s a method of allowing many customers to share a single public IP address. With CGNAT, your home router is assigned a private IP address that is sharing a public IP address with many other customers. As a result, IPV4’s limited 32-bit address space problem is stretched further.
However, the shared nature of the public IP addresses makes this strategy ineffective. Incoming traffic is not allowed; hence the created IP addresses are only relevant for outgoing traffic.
CGNAT means that your internet connection will always be a double NAT connection. You are not able to receive uninitiated requests coming from the outside. This is generally not an issue but does come with some limitations. This is especially true for gaming. Gaming often uses peer-to-peer (P2P) connections that CGNAT tends to break.
Why is CGNAT Used
CGNAT is commonly used because the current IPv4 address space only has about 4 billion IP addresses, and ISPs are exhausting their supply of addresses. The long-term plan is to transition subscribers to IPv6 addresses. However, until then, some ISPs, have chosen to use the CGNAT technique to solve the IP address scarcity problem. This is most commonly seen with cellular and satellite-based providers.
Legacy internet service providers, including most cable, DSL, or fiber-based ISPs, offer a proper public IP address. These could be dynamically assigned or statically assigned to customers. They have had these addresses since before there was really a shortage.
Newer ISPs, including Starlink, have had a tough time securing enough public IP addresses and have been effectively forced to use CGNAT.
IPv6 the Long Term Solution
Currently, Starlink now offers IPv6 support. Most cellular providers do offer varying degrees of IPv6 end-user connectivity. T-Mobile appears to be betting heavily on IPv6 taking over in the need for IPv4 entirety.
With IPv6, there are many more addresses available, and every device could theoretically have its own publicly routable IP address if desired. Some devices, such as game consoles, will definitely benefit from using IPv6 with no NAT required at all.
Conclusion: CGNAT VPN Bypass
Using a VPN service can allow you to easily bypass the impacts of CGNAT on Starlink or any other internet service provider. Setup is a breeze if you choose to use the VPN directly on your devices themselves. If you want the easiest setup possible, NordVPN is a great option.
Setting up the VPN on your router is a little more complicated but still very possible for most people with some technical skills. Finally, if you want to go full-on geeky, you can install a VPN server gateway on a cloud server such as Digital Ocean, AWS, or Google Cloud.
You will then have a proper publicly routable IP address that you can use to set up port forwarding.
